USS Marshall (DD-676) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
USS ''Marshall'' (DD-676) was a of the
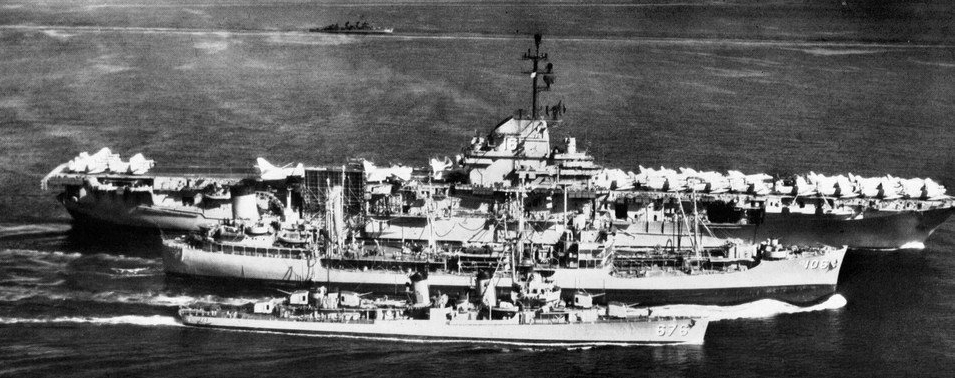 For the next 11 years, ''Marshall'' operated as a unit of the U.S. Pacific Fleet, Pacific Fleet. Homeported at San Diego, she was regularly deployed with the U.S. 7th Fleet, 7th Fleet in the western Pacific. While with that fleet she operated primarily with TF 77 and in 1960 was a unit of a carrier strike group standing by in the South China Sea during the uprising of the Communist Pathet Lao in Laos.
On 1 September 1964, ''Marshall'' changed her home port to Tacoma, Washington There she relieved as the United States Navy Reserve, Naval Reserve training ship for the 13th Naval District. On 21 October 1964, a small fire started in the substructure near the outer end of Todd Pacific Shipyards Repair Pier 7. Fueled by creosote and oil-soaked timbers, the fire soon engulfed Repair Pier 7 and quickly spread to the east wing-wall of Drydock No. 2, where ''Marshall'' was sitting high and dry, undergoing a $300,000 overhaul. The flames spread so rapidly the destroyer’s captain, Commander J. F. Stanfil Jr., ordered his 108 crewmen off the ship to join the firefighters and shipyard workers battling the fire.
With her active service completed, ''Marshall'' was stricken from the Naval Vessel Register 19 July 1969 and sold for scrapping in July 1970 to Zidell Explorations Co., Portland, Oregon for $80,596.66.
For the next 11 years, ''Marshall'' operated as a unit of the U.S. Pacific Fleet, Pacific Fleet. Homeported at San Diego, she was regularly deployed with the U.S. 7th Fleet, 7th Fleet in the western Pacific. While with that fleet she operated primarily with TF 77 and in 1960 was a unit of a carrier strike group standing by in the South China Sea during the uprising of the Communist Pathet Lao in Laos.
On 1 September 1964, ''Marshall'' changed her home port to Tacoma, Washington There she relieved as the United States Navy Reserve, Naval Reserve training ship for the 13th Naval District. On 21 October 1964, a small fire started in the substructure near the outer end of Todd Pacific Shipyards Repair Pier 7. Fueled by creosote and oil-soaked timbers, the fire soon engulfed Repair Pier 7 and quickly spread to the east wing-wall of Drydock No. 2, where ''Marshall'' was sitting high and dry, undergoing a $300,000 overhaul. The flames spread so rapidly the destroyer’s captain, Commander J. F. Stanfil Jr., ordered his 108 crewmen off the ship to join the firefighters and shipyard workers battling the fire.
With her active service completed, ''Marshall'' was stricken from the Naval Vessel Register 19 July 1969 and sold for scrapping in July 1970 to Zidell Explorations Co., Portland, Oregon for $80,596.66.
navsource.org: USS ''Marshall''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Marshall (DD-676) World War II destroyers of the United States Cold War destroyers of the United States Korean War destroyers of the United States Ships built in Kearny, New Jersey 1943 ships Fletcher-class destroyers of the United States Navy
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
.
Namesake
Thomas Worth Marshall Jr. was born on 22 December 1906 inWashington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
He attended the United States Naval Academy
The United States Naval Academy (US Naval Academy, USNA, or Navy) is a federal service academy in Annapolis, Maryland. It was established on 10 October 1845 during the tenure of George Bancroft as Secretary of the Navy. The Naval Academy ...
beginning in 1926. Following graduation in 1930, Ensign Marshall served on the battleship
A battleship is a large armored warship with a main battery consisting of large caliber guns. It dominated naval warfare in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
The term ''battleship'' came into use in the late 1880s to describe a type of ...
and received flight training at Hampton Roads, Virginia
Hampton Roads is the name of both a body of water in the United States that serves as a wide channel for the James, Nansemond and Elizabeth rivers between Old Point Comfort and Sewell's Point where the Chesapeake Bay flows into the Atlantic O ...
and Naval Air Station Pensacola
Naval Air Station Pensacola or NAS Pensacola (formerly NAS/KNAS until changed circa 1970 to allow Nassau International Airport, now Lynden Pindling International Airport, to have IATA code NAS), "The Cradle of Naval Aviation", is a United State ...
, Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
. He subsequently was an officer on board the cruiser
A cruiser is a type of warship. Modern cruisers are generally the largest ships in a fleet after aircraft carriers and amphibious assault ships, and can usually perform several roles.
The term "cruiser", which has been in use for several hu ...
s and and the destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in ...
. Lieutenant (junior grade)
Lieutenant junior grade is a junior commissioned officer rank used in a number of navies.
United States
Lieutenant (junior grade), commonly abbreviated as LTJG or, historically, Lt. (j.g.) (as well as variants of both abbreviations), is ...
Marshall was a member of the staff of Commander in Chief, Asiatic Fleet
The United States Asiatic Fleet was a fleet of the United States Navy during much of the first half of the 20th century. Before World War II, the fleet patrolled the Philippine Islands. Much of the fleet was destroyed by the Japanese by Februar ...
in 1934–1935.
Following instruction at the Submarine Base, New London, Connecticut, Marshall served on the submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
until 1937, when he began duty with the Office of Naval Communications, in Washington, D.C. Lieutenant
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations.
The meaning of lieutenant differs in different militaries (see comparative military ranks), but it is often sub ...
Marshall became Executive Officer of the destroyer in 1939 and served on it for the rest of his life. Promoted to the rank of Lieutenant Commander
Lieutenant commander (also hyphenated lieutenant-commander and abbreviated Lt Cdr, LtCdr. or LCDR) is a commissioned officer rank in many navies. The rank is superior to a lieutenant and subordinate to a commander. The corresponding rank i ...
, effective at the beginning of 1942, he was killed in action when ''Jacob Jones'' was torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, su ...
ed by ''U-578'' and sunk off Cape May, New Jersey
Cape May is a city located at the southern tip of Cape May Peninsula in Cape May County, New Jersey, United States, where the Delaware Bay meets the Atlantic Ocean. It is one of the country's oldest vacation resort destinations, and part of th ...
on 28 February 1942.
Construction and commissioning
''Marshall'' was laid down by the Federal Shipbuilding & Dry Dock Co., Kearny, N.J., 29 April 1943; launched 29 August 1943; sponsored by Mrs. Thomas W. Marshall, mother of Lt. Comdr. Marshall; and commissioned 16 October 1943.World War II
''Marshalls first big assignment came while she was still on her shakedown cruise offBermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = " Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, e ...
. Speeding from that area, she rendezvoused in mid-Atlantic with , 13 December 1943, to escort President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
back from the Big Three Conference at Tehran
Tehran (; fa, تهران ) is the largest city in Tehran Province and the capital of Iran. With a population of around 9 million in the city and around 16 million in the larger metropolitan area of Greater Tehran, Tehran is the most popul ...
(28 November to 1 December).
On 6 January 1944, ''Marshall'' departed New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
for Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It was often visited by the Naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the Re ...
, arriving on the 28th. She remained at Pearl Harbor, undergoing further training and providing escort services to battle-damaged ships returning for repairs, until mid-March. Then, with Task Group 58.2 (TG 58.2), she sailed for Majuro
Majuro (; Marshallese: ' ) is the capital and largest city of the Marshall Islands. It is also a large coral atoll of 64 islands in the Pacific Ocean. It forms a legislative district of the Ratak (Sunrise) Chain of the Marshall Islands. The ato ...
, arriving on the 20th.
The Fast Carrier Task Force
The Fast Carrier Task Force (TF 38 when assigned to Third Fleet, TF 58 when assigned to Fifth Fleet), was the main striking force of the United States Navy in the Pacific War from January 1944 through the end of the war in August 1945. The tas ...
(then 5th Fleet's TF 58, later 3rd Fleet's TF 38), with ''Marshall'' taking station in the antisubmarine screen, departed Majuro 22 March to conduct aerial sorties against Palau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the Caro ...
, 30th, and Woleai
Woleai, also known as Oleai, is a coral atoll of twenty-two islands in the western Caroline Islands in the Pacific Ocean, and forms a legislative district in the Yap State in the Federated States of Micronesia and is located approximately west-n ...
, 1 April. ''Marshall'' next participated in TF 58's strikes against Japanese installations at Wakde
Wakde is an island group in Sarmi Regency, Papua, Indonesia, between the districts of Pantai Timur and Tor Atas. It comprises two islands, Insumuar (the larger) and Insumanai (much smaller).
History
Occupied by Japanese forces in April 1942, th ...
and Hollandia in New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu
Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea).
It is a simplified version of ...
, 21 to 27 April. On the 29th, Truk was the recipient of the forces' aerial message, while on the 30th her battleship
A battleship is a large armored warship with a main battery consisting of large caliber guns. It dominated naval warfare in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
The term ''battleship'' came into use in the late 1880s to describe a type of ...
s commenced the bombardment of Ponape
Ponape may refer to:
* Pohnpei, an island in the Federated States of Micronesia
* ''Ponape'' (barque), a German sailing ship
{{disambiguation ...
and her cruiser
A cruiser is a type of warship. Modern cruisers are generally the largest ships in a fleet after aircraft carriers and amphibious assault ships, and can usually perform several roles.
The term "cruiser", which has been in use for several hu ...
s shelled Satawan
Satawan Atoll is an atoll located about southeast of Chuuk Lagoon proper.
Geographically it is part of the Nomoi or Mortlock Islands in the Carolines and administratively it is part of Chuuk State in the Federated States of Micronesia. About ...
. In May, the force moved against Wake and Marcus Island
, also known as Marcus Island, is an isolated Japanese coral atoll in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, located some southeast of Tokyo and east of the closest Japanese island, South Iwo Jima of the Ogasawara Islands, and nearly on a straight line ...
s, with ''Marshall'' assigned to join in an antishipping sweep north of the latter.
The next month, the task force was called on to support amphibious operations in the Marianas. On the 17th, the force headed west to intercept a Japanese force reported en route to the Marianas
The Mariana Islands (; also the Marianas; in Chamorro: ''Manislan Mariånas'') are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, betw ...
to support enemy troops fighting on Saipan
Saipan ( ch, Sa’ipan, cal, Seipél, formerly in es, Saipán, and in ja, 彩帆島, Saipan-tō) is the largest island of the Northern Mariana Islands, a Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), commonwealth of the United States in the western Pa ...
, Tinian
Tinian ( or ; old Japanese name: 天仁安島, ''Tenian-shima'') is one of the three principal islands of the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands. Together with uninhabited neighboring Aguiguan, it forms Tinian Municipality, one of th ...
, Guam, Rota (island), Rota, and Pagan Islands. On the 19th, the Battle of the Philippine Sea commenced. In the course of the 2-day battle, the Imperial Japanese Navy, Japanese Fleet lost three aircraft carriers and 395 carrier planes (92 percent of her carrier plane strength). ''Marshall'' was credited with an assist in splashing two of those planes. For the next month and a half, ''Marshall'' continued to support operations in the southern Marianas, interrupted only by participation in the strikes against Chichi Jima and Iwo Jima, 4 July, and against Palau, Ulithi, and Yap, 23 to 27 July.
''Marshall'' returned to Eniwetok in mid-August for voyage repairs and upkeep, departing again on the 23rd for operations in the Palau Islands. As a unit of TF 38 (formerly 58), she took part in the Palau and Philippines, Philippine operations 6 to 24 September. On 12 September, she picked up 44 Japanese survivors from , sunk 18 August by .
After repair and replenishment at newly won Ulithi, ''Marshalls task group got underway 6 October for strikes against Okinawa, 10th, and Taiwan, Formosa, 12th to 14th. ''Marshall'' was then ordered to provide antiaircraft cover for during airstrikes against enemy strongholds throughout the Philippines. On the 22d, she rejoined her task group in a search for the enemy in the Sibuyan Sea and the Mindoro Strait. On the 25th, the Task Force moved north towards Cape Engaño (Luzon), Cape Engaño, while ''Marshall'' joined TG 34.5 proceeding to San Bernardino Strait to intercept units of the Japanese Fleet withdrawing from Leyte Gulf. In the first hours of the 26th, was sighted and sunk by the group. Returning to the fast carrier force on the 31st, ''Marshall'' continued to operate in the Philippines until the end of the year.
The new year, 1945, brought further strikes against the Philippines and, with operations in the South China Sea, against Formosa and the coast of China. On 10 February, ''Marshall'', with TG 58.2, sailed for the enemy's home islands and on the 16th and 17th the carrier planes flew against Tokyo. The force then sped southeast to support the Battle of Iwo Jima, landings on Iwo Jima, returning to the Honshū area for further strikes on the 25th. By 1 March the task force was off Okinawa, commencing strikes in preparation for that campaign. On the 15th, strikes were directed against Kyūshū. On the 19th, received a direct hit and ''Marshall'' joined in the rescue, taking off 212 of her crew, and, on the 20th, escorted the listing ship back to Ulithi.
During the Battle of Okinawa, Okinawa campaign ''Marshall'' operated as advanced radar picket for her task group and escorted damaged ships to safety, 8 April to 9 May. On 9 May, she departed for Ulithi, continuing on to Leyte (island), Leyte and finally San Francisco, arriving 6 July for overhaul. Before completion, the war ended and ''Marshall'' inactivated. Decommissioned in December, she was placed in the Reserve Fleet at Naval Station San Diego, San Diego.
Post-War service
On 27 April 1951 ''Marshall'' was recommissioned and on 22 August joined TF 77 in the Sea of Japan, once more screening aircraft carriers in combat, this time against Communist forces in Korea. During this tour in the Far East, ''Marshall'' served with the Formosa Strait patrol and with the United Nations Blockade and Escort Force off Korea's east coast as well as on carrier screen duty in the Yellow Sea. In March 1952, the destroyer returned to San Diego for overhaul and on 4 October sailed again for the Far East. Arriving on 28 October, she once again began a Korean combat tour as a screening unit for carriers. In mid-November, she was detached and, after two weeks of Hunter-killer Group, hunter-killer operations, joined TF 95 in the bombardment of Wonsan on 10 December. On 7 January 1953, she steamed south to join the Formosa Strait patrol. In mid-February, ''Marshall'' rejoined TF 77. Two months later, her western Pacific deployment completed, she headed home, arriving at San Diego on 6 May.Awards
''Marshall'' received eight battle stars for World War II service and four for Korean War service.References
* *External links
navsource.org: USS ''Marshall''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Marshall (DD-676) World War II destroyers of the United States Cold War destroyers of the United States Korean War destroyers of the United States Ships built in Kearny, New Jersey 1943 ships Fletcher-class destroyers of the United States Navy